代理是实现AOP(Aspect oriented program,面向切面编程)的核心和关键技术。
概念 代理是一种设计模式,其目的是为其他对象提供一个代理以控制对某个对象的访问,代理类负责为委托类预处理消息,过滤消息并转发消息以及进行消息被委托类执行后的后续处理。为了保持行为的一致性,代理类和委托类通常会实现相同的接口
静态代理:由程序员创建代理类或特定工具自动生成源代码再对其编译,也就是说在程序运行前代理类的.class文件就已经存在。
动态代理:在程序运行时运用反射机制动态创建生成。
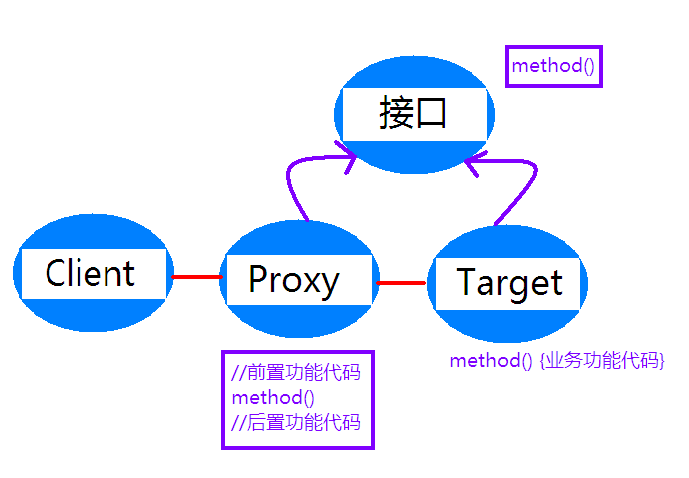
代理架构图
紫色箭头代表类的继承关系,红色连线表示调用关系
动态代理
JVM可以在运行期动态生成类的字节码,该类往往被用作动态代理类。
JVM生成的动态类必须实现一个或多个接口,所以这种只能用作具有相同接口的目标类的代理。
CGLIB库可以动态生成一个类的子类,一个类的子类也可作为该类的代理,这个可用来为没有实现接口的类生成动态代理类。
代理类可在调用目标方法之前、之后、前后、以及处理目标方法异常的catch块中 添加系统功能代码。
创建动态类 API:
java.lang.reflect:Class Proxy java.lang.reflect:Interface InvocationHandler
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 package com.iot.proxy;import java.lang.reflect.*;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collection;public class ProxyTest public static void main (String[] args) throws Exception Class clazzProxy1 = Proxy.getProxyClass(Collection.class.getClassLoader(), Collection.class); System.out.println(clazzProxy1); printConstructors(clazzProxy1); printMethods(clazzProxy1); } public static void printConstructors (Class clazz) System.out.println("-------------constructors list-------------" ); Constructor[] constructors = clazz.getConstructors(); System.out.print(getExecutableList(constructors)); } public static void printMethods (Class clazz) System.out.println("-------------methods list-------------" ); Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods(); System.out.print(getExecutableList(methods)); } public static String getExecutableList (Executable[] executables) StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); for (Executable executable : executables) { String name = executable.getName(); stringBuilder.append(name); stringBuilder.append("(" ); Class[] clazzParams = executable.getParameterTypes(); for (Class clazzParam : clazzParams) { stringBuilder.append(clazzParam.getName()).append("," ); } if (clazzParams != null && clazzParams.length != 0 ) { stringBuilder.deleteCharAt(stringBuilder.length() - 1 ); } stringBuilder.append(")\n" ); } return stringBuilder.toString(); } }
输出结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0 -------------constructors list------------- com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0(java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler) -------------methods list------------- add(java.lang.Object) remove(java.lang.Object) equals(java.lang.Object) toString() hashCode() clear() contains(java.lang.Object) isEmpty() iterator() size() toArray([Ljava.lang.Object;) toArray() spliterator() addAll(java.util.Collection) stream() forEach(java.util.function.Consumer) containsAll(java.util.Collection) removeAll(java.util.Collection) removeIf(java.util.function.Predicate) retainAll(java.util.Collection) parallelStream() isProxyClass(java.lang.Class) getInvocationHandler(java.lang.Object) getProxyClass(java.lang.ClassLoader,[Ljava.lang.Class;) newProxyInstance(java.lang.ClassLoader,[Ljava.lang.Class;,java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler) wait() wait(long,int) wait(long) getClass() notify() notifyAll()
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 private static void createProxyInstance ( ) throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException Class clazzProxy1 = Proxy.getProxyClass(Collection.class.getClassLoader(), Collection.class); Constructor constructor = clazzProxy1.getConstructor(InvocationHandler.class); Collection proxy1 = (Collection) constructor.newInstance(new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable return null ; } }); Collection proxy2 = (Collection)Proxy.newProxyInstance( Collection.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Collection.class}, new InvocationHandler() { ArrayList target = new ArrayList(); @Override public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable System.out.println("before invoke method: " +method.getName()); return method.invoke(target,args); } }); proxy2.add("aaa" ); proxy2.add("bbb" ); System.out.println(proxy2.size()); System.out.println(proxy2); System.out.println(proxy2.getClass().getName()); }
输出结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 before invoke method: add before invoke method: add before invoke method: size 2 before invoke method: toString [aaa, bbb] com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0
上述代码相关说明:
若将method.invoke(target,args);改为method.invoke(proxy,args);会出现死循环
从输出结果可知,每次调用代理类的方法,实际都是调用invoke方法
若将method.invoke(target,args);改为method.invoke(targetTmp,args);,则proxy2.size()为0。因为每次调用invoke方法时,targetTmp为新的局部变量
Object类只有的hashCode, equals, or toString方法会被交到InvocationHandler,其他方法自己有实现,不交给handler,所以最后打印结果为com.sun.proxy.$Proxy0而不是Collection
InvocationHandler接口只有一个invoke方法,每次调用代理类的方法,即调用了InvocationHandler对象的invoke方法
invoke方法涉及三个要素:
注:Object类的hashCode,equals,toString方法交给invoke,其他的Object类的方法,Proxy有自己的实现。
If a proxy interface contains a method with the same name and parameter signature as the hashCode, equals, or toString methods of java.lang.Object, when such a method is invoked on a proxy instance, the Method object passed to the invocation handler will have java.lang.Object as its declaring class. In other words, the public, non-final methods of java.lang.Object logically precede all of the proxy interfaces for the determination of which Method object to pass to the invocation handler.
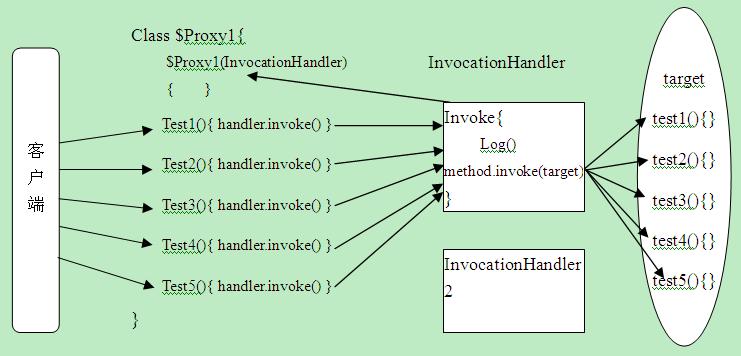
动态代理的工作原理 代理类创建时需要传入一个InvocationHandler对象,client调用代理类,代理类的相应方法调用InvocationHandler的的invoke方法,InvocationHandler的的invoke方法(可在其中加入日志记录、时间统计等附加功能)再找目标类的相应方法。
动态代理的工作原理图
面向切面编程 把切面的代码以对象 的形式传递给InvocationHandler的的invoke方法,invoke方法中执行该对象的方法就执行了切面的代码。
所以需要传递两个参数:
1.目标(Object target)
定义Advice接口
1 2 3 4 public interface Advice void beforeMethod (Method method) void aftereMethod (Method method) }
一个实现Advice接口的类MyAdvice,用于打印执行方法前和执行后的时间
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 import java.lang.reflect.Method;public class MyAdvice implements Advice long beginTime = 0 ; @Override public void beforeMethod (Method method) System.out.println(method.getName()+" before at " +beginTime); beginTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); } @Override public void aftereMethod (Method method) long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(method.getName()+" cost total " + (endTime-beginTime)); } }
定义一个getProxy方法创建实例对象,接收两个参数:目标和通知
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 private static Object getProxy (final Object target,final Advice advice) Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance( target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), new InvocationHandler() { @Override public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable advice.beforeMethod(method); Object retVal = method.invoke(target,args); advice.aftereMethod(method); return retVal; } } ); return proxy; }
调用:
1 2 3 4 Collection proxy3 = (Collection) getProxy(new ArrayList(),new MyAdvice()); proxy3.add("111" ); proxy3.add("222" ); System.out.println(proxy3.size());
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 add before at 0 add cost total 0 add before at 1454433980839 add cost total 0 size before at 1454433980839 size cost total 0 2
参考资料